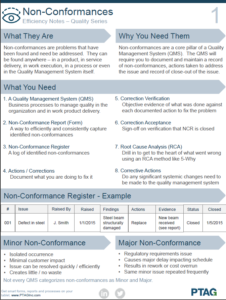
Non-conformances
Non-conformances are problems that have been identified and require resolution. These issues can arise in various areas, such as project planning, project delivery, maintenance, work execution, and even within the Quality Management System (QMS) itself. Non-conformances are a critical aspect of any QMS.
At PTAG, we recognize the significance of addressing non-conformances and offer a dedicated service to help you with industry best practices, planning, execution and monitoring. Our team of QMS experts will collaborate with you to identify gaps in your current non-conformance processes, take necessary actions to address them, and keep track of their resolution.
Our ultimate goal is to assist you in developing an efficient and effective Quality Management System that meets all applicable standards and regulatory requirements.
What You Need
1. A Quality Management System (QMS)
Business processes to manage quality in the organization and in work product delivery.
2. Non Conformance Report (Form)
A way to efficiently and consistently capture identified non conformance.
3. Non Conformance Register
A log of identified non conformance.
4. Actions / Corrections
Document what you are doing to fix it.
5. Correction Verification
Objective evidence of what was done against each documented action to fix the problem.
6. Correction Acceptance
Sign-off on verification that NCR is closed.
7. Root Cause Analysis (RCA)
Drill in to get to the heart of what went wrong using an RCA method like 5-Why. There are many different methods of root cause analysis.
8. Corrective Actions
Do any significant systemic changes need to be made to the quality management system
Non Conformance Register
The table below is an example of what a non conformance register may look like:

Anatomy of a Non Conformance Report
The form below is an example of what a non conformance report may look like:
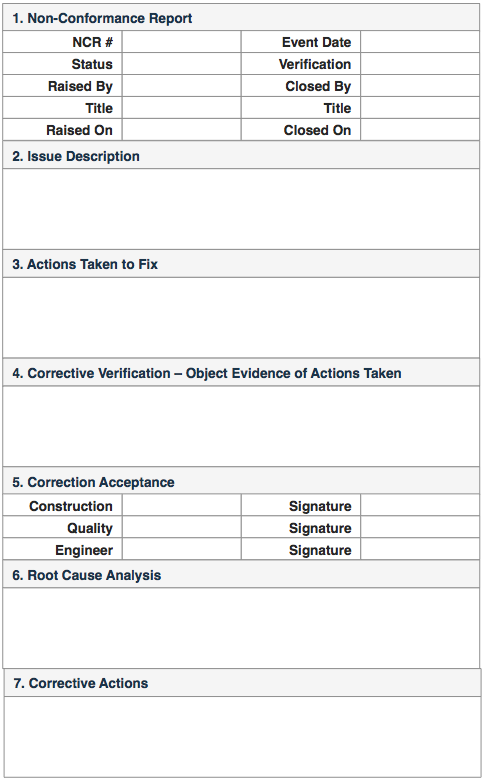
1. The general details of the non conformance. Identify who found the issue and important dates toward close. QMS may require someone to actually accept the NCR.
2. Describe NCR in enough detail that someone not at the point of the event can read and understand exactly what it is and what should be done.
3. Damage control – what are you doing immediately to address the issue.
4. What objective evidence was reviewed to confirm the actions were taken and the issue can be closed out.
5. Sign-off typically required by the people responsible for reviewing the objective evidence of actions taken.
6. The organization may decide to undertake a deeper systemic analysis to prevent future occurrences.
7. The RCA may result in corrective actions – process-level changes to prevent recurrence of non conformances like this.
Download this Reference Guide, print it off and take it with you so that you always have at your fingertips a quick primer on project risk management.